01. Roles and Permissions
Principals
Principals are entities that can request SQL Server resources.
SQL Server-level principals
- SQL Server authentication Login
- sa
- Created when instance is installed
- Default database is
master - Member of
sysadmindatabase role
- public
- Every login belongs to the this role
- Windows authentication login for a Windows user
- Windows authentication login for a Windows group
- Azure Active Directory authentication login for a AD user
- Azure Active Directory authentication login for a AD group
- Server Role
Database-level principals
- Database User (There are 11 types of users. For more information, see CREATE USER.)
- dbo
- Created for each database
- Has all permissions in the database
- Owns
dboschema (dboschema is the default schema for all users, and cannot be dropped)
- guest
- Permissions granted are inherited by users who have access to the database, but who do not have a user account in the database.
- Cannot be dropped
- Can be disabled by revoking it's CONNECT permission (
REVOKE CONNECT FROM GUEST;)
- Database Role
- Application Role
Special Schemas
INFORMATION_SCHEMA
sys
Server-Level Roles and Permissions
Fixed Roles
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| sysadmin | Can perform any activity in the server. |
| serveradmin | Can change server-wide configuration options and shut down the server. |
| securityadmin |
|
| processadmin | Can end processes that are running in an instance of SQL Server. |
| setupadmin | Can add and remove linked servers by using Transact-SQL statements. (sysadmin membership is needed when using Management Studio.) |
| bulkadmin | Can run the BULK INSERT statement. |
| diskadmin | Used for managing disk files. |
| dbcreator | Can create, alter, drop, and restore any database. |
| public |
|
Fixed Roles and Permissions
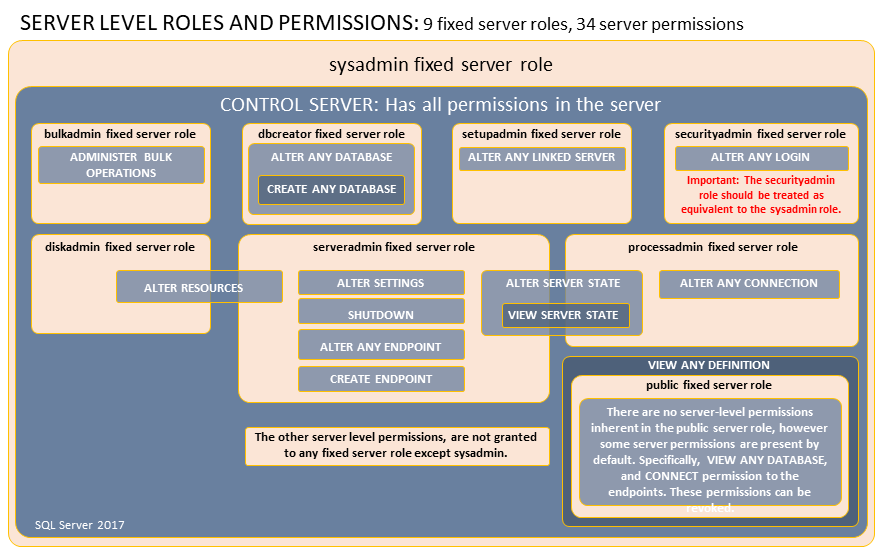
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/security/authentication-access/server-level-roles?view=sql-server-2017
Working with Server-Level Roles
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/security/authentication-access/server-level-roles?view=sql-server-2017#working-with-server-level-roles
Database Level Roles and Permissions
CREATE LOGIN ... WITH PASSWORD = ...;
Fixed Roles
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| db_owner |
|
| db_securityadmin |
|
| db_accessadmin | Can add or remove access to the database for Windows logins, Windows groups, and SQL Server logins. |
| db_backupoperator | Can back up the database. |
| db_ddladmin | Can run any Data Definition Language (DDL) command. |
| db_datawriter | Can add, delete, or change data in all user tables. |
| db_datareader | Can read all data from all user tables. |
| db_denydatawriter | Cannot add, modify, or delete any data in the user tables within a database. |
| db_denydatareader | Cannot read any data in the user tables within a database. |
Fixed Roles and Permissions
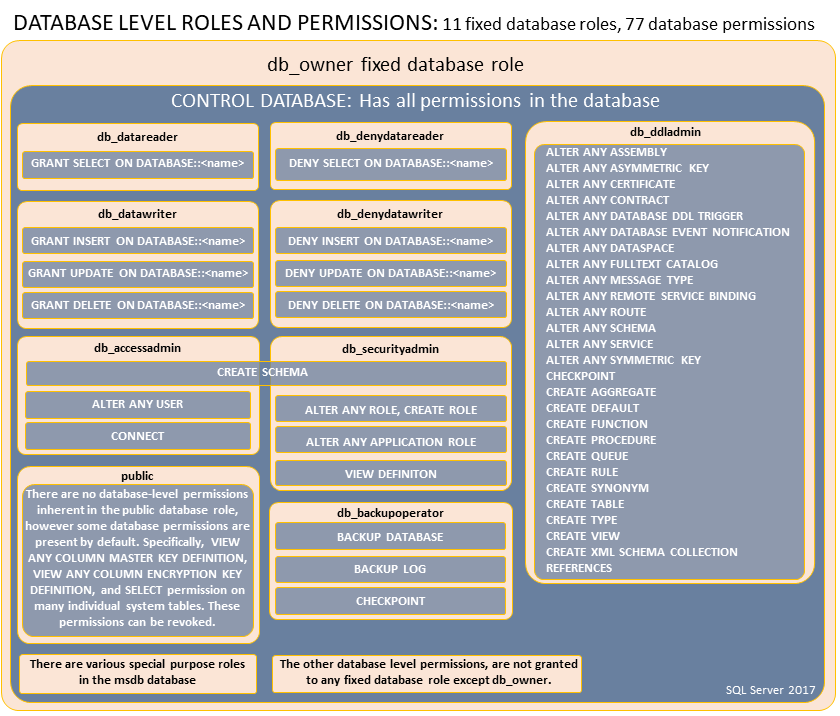
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/security/authentication-access/media/permissions-of-database-roles.png?view=sql-server-2017
Special Roles for SQL Database and SQL Data Warehouse
- Exist only in the virtual master database.
-
Permissions are restricted to actions performed in master.
-
Only database users in master can be added to these roles.
- Logins cannot be added to these roles, but users can be created based on logins and then those users can be added to the roles. Contained database users in master, can also be added to these roles.
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| dbmanager |
|
| loginmanager | Can create and delete logins in the virtual master database. |
msdb Roles
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| db_ssisadmindb_ssisoperatordb_ssisltduser |
|
| dc_admin dc_operatordc_proxy |
Can administer and use the data collector. |
| PolicyAdministratorRole |
|
| ServerGroupAdministratorRoleServerGroupReaderRole | Can administer and use registered server groups. |
| dbm_monitor |
|
[1] These roles can modify Integration Services packages and Integration Services packages can be executed by SQL Server using the sysadmin security context of SQL Server Agent. To guard against this elevation of privilege when running maintenance plans, data collection sets, and other Integration Services packages, configure SQL Server Agent jobs that run packages to use a proxy account with limited privileges or only add sysadmin members to the db_ssisadmin and dc_admin roles.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/security/authentication-access/database-level-roles?view=sql-server-2017#msdb-roles
R Services
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| rpkgs-users | Allows using any shared packages that were installed by members of the rpkgs-shared role. |
| rpkgs-private |
|
| rpkgs-shared |
|
Working with Database-Level Roles
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/security/authentication-access/database-level-roles?view=sql-server-2017#working-with-database-level-roles
Application Roles
- Enable access to specific data to only those users who connect through a particular application.
- Enabled by using sp_setapprole